Have you ever thought about building your own computer? There are a lot of complicated parts and tech terms that go into building a PC. For many people, it is more than just saving money or getting a custom setup. You can really enjoy this hands-on adventure into the heart of modern technology. Even though hardware is pushing the limits faster than ever in 2025, building your own PC still gives you the most control over how it looks, how well it works, and how easily you can upgrade it in the future. This guide cuts through the clutter and shows those who are ready to start this exciting project the way.
Why Build When You Can Just Buy? The Real Perks

Tailored Performance, No Compromises
There are often trade-offs with pre-built PCs. They could have a great graphics card, but skimp on a faster hard drive or a cooling system that does not work as well. Those trade-offs are out the window when you build your own PC. You pick out each and every part and make sure they all fit together so well. In other words, it is a system that really works best for what you do, whether it is intense gaming, heavy video editing, or complicated data processing. With this level of direct control, you can get better performance and get the most power out of your investment.
Smart Savings Over Time
It may seem like the cost of parts at first is about the same as buying a system already put together, but the long-term savings from building are huge. You do not have to buy a whole new computer if a part breaks or gets old. You just need to replace that one part. This design makes your PC last longer, which will save you money in the long run. Also, when parts are on sale, you can often get better deals, and you can build a stronger machine for the same amount of money.
Learning by Doing: A Skill for Life
Building a PC is a great way to learn new things. You will learn about how to keep things cool, make sure they work with each other, and the complicated dance that hardware and software do together. Not only is it fun to show off, but it also teaches you real troubleshooting skills and makes you appreciate new technology more. Taking a complicated machine and making it easy to understand is a great journey.
The Core Parts: How to Choose the Best Parts for Your Dream Machine
Just like building a skyscraper requires careful planning, picking the right parts is also very important. You need to know how each part works with the others and how it fits into the whole, not just whether it is the most expensive. There is more power and better performance in PC hardware than ever in the year 2025. Do not worry about what else is out there.
The Central Processing Unit (CPU): The Operational Brains
There is a part of a computer called the central processing unit (CPU) that does all the thinking and following through on commands. Both Intel and AMD are always pushing the limits in their long-running battle. The 13th-Gen Core series from Intel and the Ryzen Zen 4 processors from AMD are always at the top of the list for desktop performance, as shown in Tom’s Hardware’s CPU Benchmarks and Hierarchy from July 2025. Because they work so well for games, many gamers still swear by AMD’s X3D chips, such as the Ryzen 7 7800X3D. To the people on Reddit r/PcBuild in January 2025, this was a big deal. While Intel’s Core i7-14700K is more balanced and often the best choice for work.
Motherboard: The Nerve Center
All of your computer’s parts can talk to each other because of the motherboard, which is like the brain. Actually, compatibility is very important here; it is a must. A motherboard with the right CPU socket, like Intel’s LGA 1700 or AMD’s AM5, is needed. Chipsets are also very important because they manage how data moves between the CPU and the rest of the system. One of the options they give you is the type of USB ports and the number of PCIe lanes. Formats, like ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX, come next. The motherboard size is determined by these, and the PC case size is determined by the motherboard size. PCIe 5.0 is supported by a lot of new motherboards for 2025. This is a big deal for the newest graphics cards and NVMe SSDs, according to many tech sites.
Graphics Card (GPU): Your Visual Powerhouse
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is probably the most important part of a computer for people who like to play games or make art. It makes all those beautiful pictures, videos, and animations possible, which has a direct effect on how well things run and look. As of July 2025, the GPU Benchmarks Hierarchy on Tom’s Hardware is the best place to find full rankings of Nvidia, AMD, and Intel graphics cards. Leading the way are Nvidia’s RTX 50 series and AMD’s RX 9000 series. The GPU like the RTX 5070 and RX 9070 XT offer great performance at a range of price points. For 4K gaming, you should probably look at higher-end cards like the RTX 5080 or AMD 7900XT/XTX. Just make sure you can get them at the recommended retail price to get the best deal. As Geekawhat pointed out in February 2025, Intel’s Arc B570 has also come a long way. Its performance has improved a great deal, making it a good choice, especially if you are on a tight budget.
RAM (Random Access Memory): The PC’s Short-Term Memory
It stores data that your CPU needs to get quickly. RAM is like the quick-access memory on your PC. How fast your PC is and how snappy your apps feel are directly related to how much RAM you have and how fast it is. DDR5 RAM has become the standard in 2025, offering much faster speeds and more space than its older sibling, DDR4. In July 2025, Corsair made a very strong case for why DDR5 is the best choice for high performance, especially in games, where some users saw their average frame rates jump by as much as 31%. Many games still work fine with 16GB of DDR5 RAM, but 32GB is quickly becoming the best choice for serious streamers, content creators, and anyone who wants to make sure their setup will work in the future, as BattleforgePC pointed out in July 2025. DDR5 kits start at about 4800MHz, and the fastest ones go up to 6000MHz or even higher, which is a huge speedup for data.
Storage: SATA SSDs, NVMe SSDs and Good Old HDDs
The type of storage you choose affects how quickly your OS starts up, your apps open, and you can send and receive files. Even in 2025, people are still trying to make storage faster and smaller. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) SSDs are much faster than older SATA SSDs. They connect directly to your motherboard through PCIe lanes. Expert Market Research says that NVMe SSDs are very popular because they clearly perform better than other types of SSDs. An NVMe SSD is a must-have for hard tasks and lightning-fast boot times. Some Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are still the most affordable way to store huge amounts of files, while SATA Solid State Drives (SSDs) still offer a balance of speed and price for general storage. Just do not count on them being fast enough for your operating system or the apps you use most. AI workloads need very fast speeds and few delays, which is why PCIe 5.0 SSDs are becoming more popular, according to Semiconductor Insight in April 2025. For high-end builds, these are definitely something to think about.
If you’re not sure which storage type suits your build, check out this detailed guide on SSD vs HDD: Which Is the Right Storage for You?
Power Supply Unit (PSU)
The Power Supply Unit (PSU) is often the hero of a PC build that does not get much attention. It is easy to forget, but it is very important if you want your system to stay stable and work for years. This device changes the AC power from the wall into the DC power your electronics need. The wattage and efficiency rating of a PSU are the two most important things to look for. The wattage should be enough to power everything you have. Most of the time, these ratings come with an 80 PLUS rating, such as Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum, or Titanium. These certifications show how well the PSU changes power, which means it wastes less energy and makes less heat. Tom’s Hardware says that most modern PSUs work most efficiently when they are running at about half of their rated capacity as of July 2025. As reported by TechSpot, a new 80 Plus Ruby PSU efficiency rating was released in May 2025. This rating is even better than Titanium standards. With this new standard, systems must be 90% efficient even when they are only 5% loaded. This is a huge improvement over the systems we have now. Always choose a PSU with more wattage than your system needs, and always try to get one with a higher efficiency rating.
The PC Case: More Than Just a Box
A PC case is more than just a pretty box; it is an important part of how your system looks, how well it cools, and how you manage your cables. When you choose one, check to see if it fits the size of your motherboard (ATX, Micro-ATX, or Mini-ITX), if it has enough space for your graphics card and CPU cooler, and how well it moves air. GamesRadar+ showed off some cool new designs from Computex in June 2025. The designs really focused on better airflow and modularity. Nowadays, many cases come with tempered glass panels that let your cool parts shine through and RGB lighting for that extra touch of style. But do not forget that function comes first. A case with good airflow and lots of room to organize cables will make your system cooler, quieter, and easier to keep up. A big deal is also the trend of needing more space for bigger GPUs and better cooling. This is especially true for next-generation graphics cards, which are getting stronger and need a lot of cooling, according to Antec India in February 2025.
CPU Coolers and Case Fans: Keeping Your System Chilly
To get the best performance and make your PC last longer, it is very important to keep your parts cool. A CPU cooler is a must-have for your computer because your CPU gets very hot when it is working hard. You can choose between air coolers, which use fans and heatsinks, and liquid coolers (AIOs or custom loops), which move coolant around to reduce heat. Case fans are just as important; they move air around inside your case by pushing hot air out and bringing cool air in. What makes a big difference in how hot your system is is how many fans you have, how big they are, and where you put them. For 2025, fan technology is all about making them run more quietly and improving static pressure, which is important for moving air through radiators and other parts that are close together. If you manage your parts’ temperature well, they will work at their best, not slow down from getting too hot, and they will last longer.
Building Your PC: A Step-by-Step Adventure
It might look like there are a lot of pieces to putting together a PC, but the steps are actually very clear. It is pretty easy to do once you get the hang of it. This part walks you through the most important steps to make sure your build goes smoothly.
PC Part Compatibility Checking
Make sure that all of your parts work together before you even open the box. The socket type on both your CPU and motherboard must be the same. The RAM you buy needs to be compatible with your motherboard (DDR4 or DDR5). So make sure your graphics card has enough room in its case and that it gets enough power from the power supply. This is where sites like PCPartPicker.com come in handy. You can choose all of your parts, and it will show you any known problems with compatibility. In the long run, this step will save you a lot of trouble.
The Build Itself: Bringing Your Vision to Life
- Prep Your Space: Find a place that is clean, well-lit, and has lots of space. You can wear a wrist strap that does not conduct electricity, or you can just touch your PC case or something else metal and grounded a lot. This gets rid of any static electricity that might damage your electronics.
- CPU Time: Open the CPU socket lever on your motherboard slowly. Place the CPU so that it lines up with the small triangle or arrow on the socket. Then, carefully drop it in. There can be no forcing! To lock it down, close the lever.
- Cooler Install: If your CPU came with a cooler, follow the directions that came with it. Before you install an aftermarket cooler, make sure there is thermal paste in the middle of the CPU (if it is not already there). Then, follow the instructions on how to mount the cooler. Make sure it fits well and is even.
- RAM In: Look on your motherboard for places to put RAM. Open up the clips on both ends of a slot. Put the RAM stick in the slot so that it lines up with the notch. Then, press down hard and evenly on both ends until the clips close.
- Motherboard Mount: Put the standoffs in your PC case and screw them in place. These mounts are small enough to fit on top of your motherboard. Carefully place the motherboard on top of them so that the screw holes line up. Use screws to hold it down.
- GPU Power: On your motherboard, open the PCIe slot clip. Press down hard on the slot until you hear a click. Make sure the graphics card falls into place. To keep it steady, screw it into the case.
- Storage Setup: NVMe SSDs usually just stick on the motherboard, sometimes under a heatsink. Your case probably has drive bays where you can slide SATA SSDs and regular hard drives in. You can connect the SATA power cables from your power supply to your motherboard and the SATA data cables to your motherboard.
- PSU Connection: Put your power supply where it belongs in the case. Connect your graphics card, storage drives, and fans to the main power cables that come from your motherboard. The main power cables have 24 pins and 8 pins for the CPU.
- Case Cables: Connect the tiny cables on the front of your case that go to the power button, reset button, USB ports, and audio jacks to the correct pins on your motherboard. For exact places, your motherboard manual is your best friend.
- Cable Tidy-Up: Put your cables neatly behind the motherboard tray or through the holes in your case. Cable management is not just for looks; it also helps air flow and makes it easy to make upgrades in the future.
⚠️ Rookie Mistakes to Dodge: Smooth Sailing Ahead
- The Missing I/O Shield: This metal plate goes into the back of your case before the motherboard. A cover goes over the ports to keep dust out. Do not forget!
- Thermal Paste Mishaps: You can not cool down if you have too much or too little. It is usually best to have a small blob about the size of a pea in the middle of the CPU.
- Loose Connections: Completely push in all of your power cables, RAM, and graphics card. A PC often will not start up because the connection is not tight.
- Cable Chaos: Having a lot of cables can make working inside your PC difficult, but it will not stop it from working.
- Plugging Monitor into the Wrong Spot: It takes place more often than you think! If you are not using integrated graphics, you should always plug your display cable into your graphics card and not the video output on your motherboard.
What Does a PC Build Cost? Your 2025 Budget Guide
Custom-built PC prices can vary a lot, depending on what level of performance you want and how much money you have to spend. Ups and downs in the supply chain, new technologies, and market demand can all cause component prices to change a lot in 2025. Here is a general list to help you decide how much to invest:
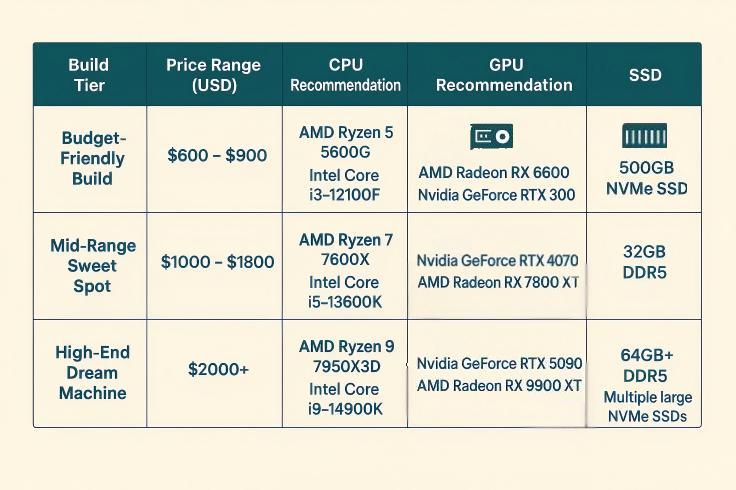
The Budget-Friendly Build: Around $600 – $900
If you are trying to save money, a PC in this price range can still run games smoothly at 1080p and do all of your other daily tasks without any problems. Here you will mostly find entry-level CPUs and motherboards, such as an AMD Ryzen 5 5600G or an Intel Core i3-12100F. It is likely that you will get 16GB of DDR4 RAM, but DDR5 is becoming more common even at this level. You will also likely get a 500GB NVMe SSD, an AMD Radeon RX 6600 or Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050 graphics card, and 16GB of DDR4 RAM. The goal is to get the most for your money, which usually means looking for sales on individual parts.
The Mid-Range Sweet Spot: Around $1000 – $1800
This is where most people who build PCs find the best deal and best performance. By 2025, a mid-range PC should be able to handle 1440p games with high refresh rates as well as more demanding tasks like editing videos or streaming. Expect a motherboard with lots of features and a CPU that is faster, like an AMD Ryzen 7 7600X or an Intel Core i5-13600K. Most likely, you will need 32GB of DDR5 RAM, a powerful GPU like an Nvidia GeForce RTX 4070 Super or an AMD Radeon RX 7800 XT, and a fast 1TB NVMe SSD. This level provides a big improvement in performance without going too far into the ultra-high-end price range.
The High-End Dream Machine: $2000 and Up
For people who only want the best—think buttery-smooth 4K gaming, making professional-quality content, or doing a lot of data analysis—this is the place to be. Extremely fast CPUs and motherboards are available here, including the AMD Ryzen 9 7950X3D and the Intel Core i9-14900K. It should have at least 64GB of lightning-fast DDR5 RAM, a top-of-the-line GPU like an Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 or an AMD Radeon RX 9900 XT, and several large NVMe SSDs for all your storage needs. A lot of the time, these builds have premium cases and custom liquid cooling setups that push the limits of what a regular PC can do.
Don’t Forget the Extras: Hidden Costs to Consider

There are costs that can sneak up on you besides the main ones. For instance, a license for the Windows operating system can add a big chunk to your budget. After that, there are the peripherals. You need a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and speakers. Some of these you may already have, but you might want to get new ones to match the power of your new PC. Do not forget to buy licenses for your favorite productivity suites or games, as well as a good surge protector to protect your investment.
Powering On and Software Setup: Bringing Your Creation to Life
After all that careful work putting your PC together, the big moment arrives: turning it on for the very first time. This is where your hardware masterpiece transforms into a working computer, ready for anything you throw at it.
The First Boot: Diving into BIOS/UEFI
Once all the parts are in place and all the cables are connected, it is time for the first power-up. Get your monitor, keyboard, and mouse set up. Start up your case by pressing the power button. You should see a brand logo or a message telling you to press a key to enter the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) if everything is okay. The BIOS or UEFI is like the brain of your PC before the operating system starts. It is the low-level software that makes your hardware talk to each other. During startup, you usually get into it by pressing a certain key over and over. Depending on the maker of your motherboard, this key is usually Del, F2, F10, or F12. You can make sure that all of your hardware is recognized in the BIOS/UEFI, change the boot order so that the media that came with your operating system is first, enable XMP/DOCP so that your RAM runs at the speed it is supposed to, and change other system settings. Explore at your own pace, but do not make any changes until you are sure.
Installing Your Operating System: Windows or Linux?
Setting the boot order and recognizing your hardware are the first steps in installing your operating system. Windows will be that for most people. You will need a USB drive with a Windows installation image on it. Microsoft’s Media Creation Tool can help you make one. After you restart your PC and plug in the USB drive, it should start up right from the drive. To install Windows, just follow the on-screen instructions and make sure to choose your main NVMe SSD. Ubuntu and other Linux distributions are pretty easy to set up if you are really into them. It is important to have your installation media ready and set up so that your BIOS or UEFI can start from it.
Drivers and Software: Unleashing Full Power
Your PC is not quite at its fastest even after you install your operating system. Installing drivers is the next very important step. Drivers are software programs that make it possible for your operating system and hardware to talk to each other correctly. If you do not have them, your graphics card might not show full resolution, your internet might not work, or your sound might not work at all. Install the chipset drivers for your motherboard first, then the drivers for your graphics card (always get these from Nvidia, AMD, or Intel’s websites). After that, install any other drivers for your peripherals that you need. There is even utility software from many motherboard makers that can help automate some of this driver installation. This is the last step. Install the software you need, such as a web browser, an antivirus program, and any work or play apps. Also, do not forget that keeping your drivers up to date is important for stability and performance.
Specialized Builds: Crafting Your Machine for Your Passion
While the basic rules of PC building stay pretty consistent, specific uses often call for a custom touch. Whether you’re chasing the highest frame rates or trying to fit a powerful machine into a tiny space, understanding these little details can turn your build from good to absolutely amazing.
Building a Gaming PC: What Really Matters
This is what you should think about when building a gaming PC: how to get the most out of your digital worlds. This means that you will put more of your attention on certain parts. In this case, your graphics card (GPU) is clearly the king. How good your games look and how smoothly they run depend on it. Spend as much money as you can on the best graphics card you can find. It will make a huge difference in how much fun you have playing games. Along with that powerful GPU, you will need fast RAM. In 2025, DDR5 with low CAS latency is the best choice. This makes sure that data gets to your CPU and GPU quickly, so there are no annoying slowdowns. A very fast NVMe SSD is also necessary so that games load quickly, so you do not have to wait as long between intense gaming sessions. Do not forget your screen either! You need a display with a high refresh rate (144Hz or more) to really see and feel how responsive and smooth your powerful gaming rig is. It is the last piece that turns powerful hardware into an exciting game experience.
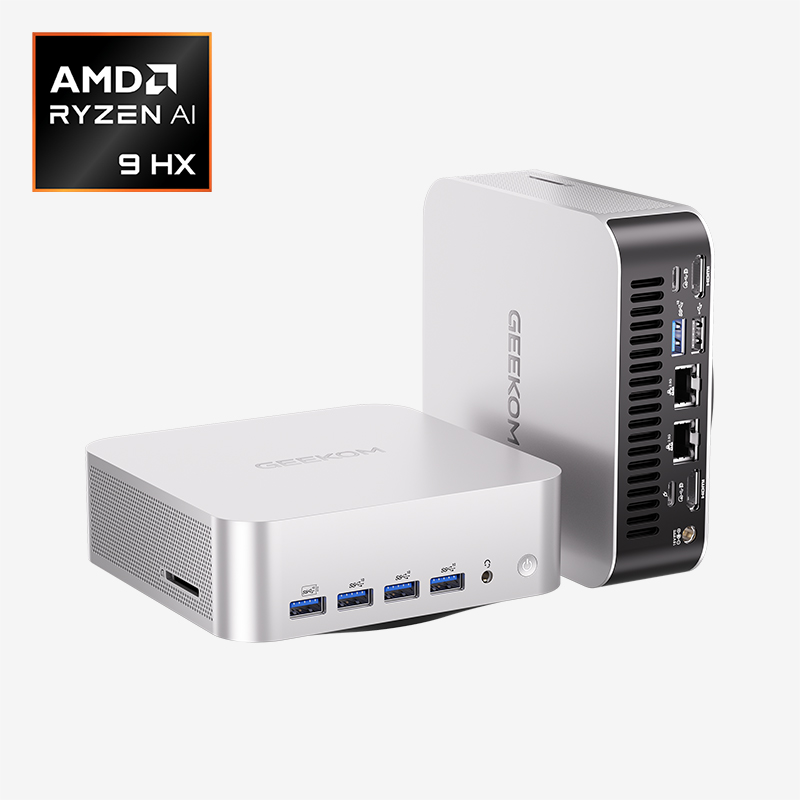
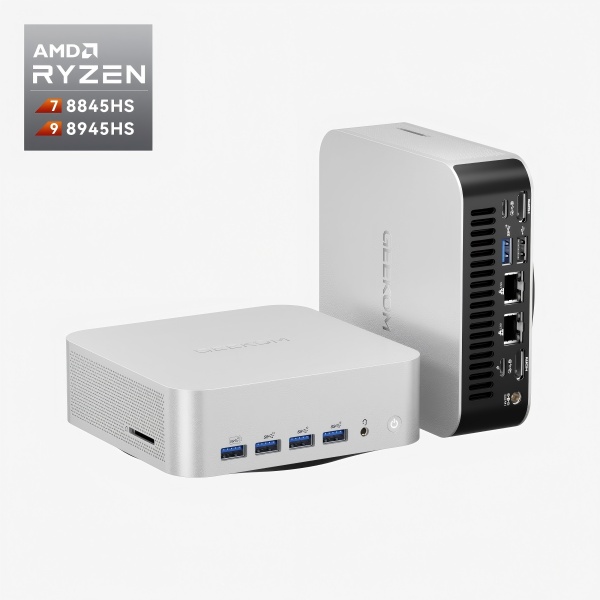
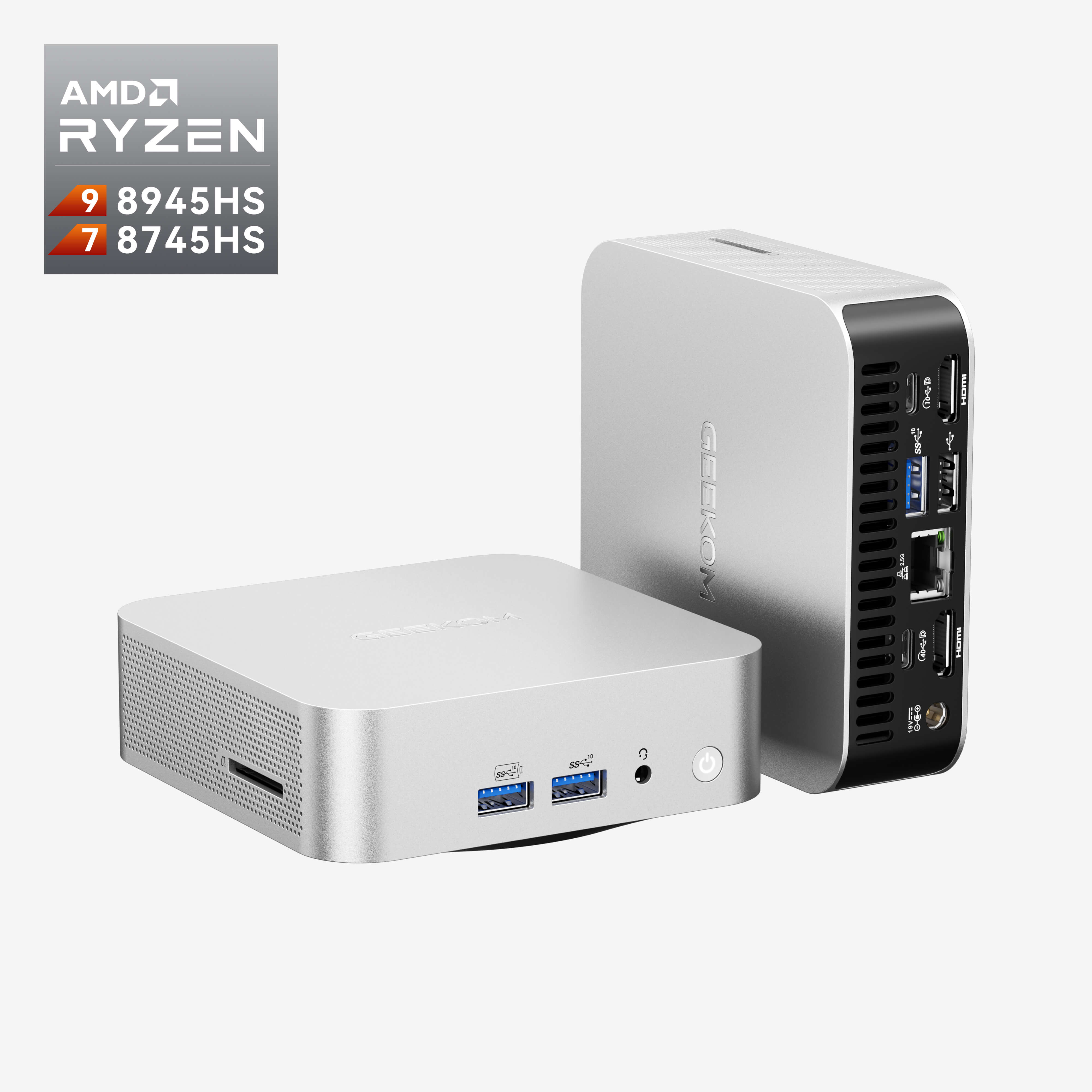
Mini PC: Small Form Factor, Big Power

For people who do not have much desk space or just want a powerful computer that does not look like a “gaming rig,” Small Form Factor (SFF) PCs are a stylish option. Making a mini PC is fun and can be hard at the same time. It will be working with motherboards called ITX that are much smaller than ATX boards. You will also need SFX power supplies that are smaller than their ATX cousins. Here, every millimeter matters, so it is very important to check the clearance between the parts. You should carefully measure the CPU cooler and graphics card you want to use to make sure they will fit in your SFF case. It is also more important to keep things cool in smaller cases, so it is very important to have good cooling solutions and airflow. Therefore, buying a mini PC is a great option to avoide those issues you may concern about.
GEEKOM provide a wide range of mini PC options that combine compact size with impressive performance. These pre-built systems are designed with optimal airflow, efficient cooling, and carefully selected hardware to ensure reliability in a small footprint. Whether you need a quiet workstation for productivity, a media center for streaming, or a capable machine for light gaming, GEEKOM’s lineup covers various performance tiers and price points.